This comprehensive guide will delve into various Ampicillin aspects crucial for patients considering this medication.
We'll begin by assessing the need for Ampicillin in your case, then explain the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and how it influences dosage requirements. Additionally, we'll evaluate potential side effects associated with using Ampicillin and discuss necessary storage conditions to ensure optimal efficacy.
Furthermore, our discussion will cover monitoring treatment progress using Ampicillin for UTIs or other infections. We will also explore its mechanism of action, safety during pregnancy, and contraindications to be aware of before you buy Ampicillin. Finally, we will compare it with Amoxicillin – another commonly prescribed antibiotic.
Table Of Contents: Buy Ampicillin
- Table of Contents: Buy Ampicillin
- I. Assessing the Need for Ampicillin
- II. Understanding Dosage Requirements
- III. Evaluating Potential Side Effects
- IV. Ensuring Proper Storage Conditions
- V. Monitoring Treatment Progress
- VI. Ampicillin for Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- VII. Ampicillin Mechanism of Action
- VIII. Ampicillin Contraindications
- IX. Ampicillin vs. Amoxicillin: Understanding the Differences
- X. Buy Ampicillin Now
I. Assessing the Need for Ampicillin
Before beginning any antibiotic therapy, evaluating if Ampicillin is required for a particular medical issue is essential. Antibiotics are potent drugs that target bacterial illnesses and must be used cautiously to help avoid contributing to antibiotic resistance.
A. Identifying Bacterial Infections
To confirm the cause of your infection is bacterial, you must rule out a viral or fungal origin. While antibiotics like Ampicillin are effective against many types of bacteria, they do not affect viral or fungal infections such as colds, flu, or yeast infections.
- Symptoms: Some common symptoms of bacterial infections include fever, chills, fatigue, and localized pain or swelling at the site of infection.
- Laboratory tests: Your healthcare provider may order laboratory tests such as blood cultures or swabs from the infected area to identify the presence of bacteria and determine their susceptibility to various antibiotics.
B. Consulting a Healthcare Professional
If you suspect a bacterial infection requiring antibiotic treatment with Ampicillin, consulting a healthcare professional is essential in making an informed decision about your care plan. They will assess your symptoms and medical history before prescribing an appropriate course of action based on factors such as the severity and duration of the illness.
C. Considering Personal Factors Affecting Treatment Choices
When determining the need for Ampicillin, it is essential to consider any personal factors that may affect your treatment choices. These can include:
- Allergies: Ampicillin may not suit you if you have a known allergy to penicillin or other beta-lactam antibiotics.
- Pregnancy and breast-feeding: While generally considered safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding, always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new medication in these situations.
- Other medications: Inform your healthcare provider of all prescription and over-the-counter medications you are currently taking, as some drugs may interact negatively with Ampicillin.
In conclusion, assessing the need for Ampicillin involves confirming the presence of a bacterial infection through symptoms and laboratory tests and consulting a healthcare professional about appropriate treatment options based on individual factors such as allergies or pregnancy status. By making informed decisions regarding antibiotic use, we can help prevent the development of antibiotic resistance while ensuring effective treatment outcomes. Ampicillin has a minimum inhibitory concentration that makes it effective against many types of bacteria. Still, it should only be used when necessary and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
It is essential to assess the need for Ampicillin before beginning any treatment. Moving on, it is equally necessary to understand dosage requirements when taking this medication.
To ensure the responsible use of antibiotics and prevent antibiotic resistance, it is crucial to assess the need for Ampicillin by confirming a bacterial infection through symptoms and laboratory tests, consulting with a healthcare professional about appropriate treatment options based on individual factors such as allergies or pregnancy status, and considering personal factors that may affect treatment choices. Prevention is better than a cure; this is the essence of wise healthcare decisions.
II. Understanding Dosage Requirements
Learning about the correct dosage of Ampicillin for your needs is crucial to ensure its effectiveness and safety during treatment. The dosage should be adjusted according to factors such as the type and severity of infection, age, weight, and overall health condition.
A. Factors Affecting Dosage
- Type of infection: Different bacterial infections require different dosages of Ampicillin. For instance, a UTI may necessitate a dosage less than prescribed for an intense respiratory infection.
- Age: Children typically require smaller doses than adults due to their developing bodies and immune systems.
- Weight: Heavier individuals may need higher doses than those with lower body weights because the drug's distribution in the body can be affected by size.
- Kidney function: People with impaired kidney function might require adjustments in their dosage since Ampicillin is primarily eliminated through the kidneys (source).
B. General Guidelines for Dosage
The following are general guidelines for adult dosages; however, it is essential to consult your healthcare provider before starting any antibiotic therapy:
- Mild-to-moderate infections: Usually prescribed at 250-500 mg every six hours orally or intramuscularly (IM).
- Severe infections: May necessitate up to one gram every four hours intravenously (IV) (source).
- Prophylactic use (e.g., before dental procedures): A single dose of two grams orally one hour before the procedure is typically recommended.
For optimal treatment outcomes, it is essential to heed your healthcare provider's instructions for dosage recommendations. It's crucial to follow their instructions carefully to ensure optimal treatment outcomes.
C. Importance of Adherence
Adhering to the prescribed dosage schedule ensures Ampicillin's effectiveness and prevents antibiotic resistance. Skipping doses or stopping treatment prematurely can lead to incomplete eradication of bacteria, increasing the risk of recurrence and the development of resistant strains (source). Always complete the entire course as directed by your healthcare provider, even if symptoms improve earlier than expected.
It is essential to comprehend the dosage of Ampicillin before use to avert any possible adverse reactions. It is, therefore, necessary for patients to evaluate the potential side effects that may occur when taking this medication.
Knowing the exact amount of Ampicillin needed for successful and secure treatment is vital. Factors such as type of infection, age, weight, and kidney function affect the appropriate dosage. Adherence to prescribed dosages is essential to prevent antibiotic resistance and completely eradicate bacteria.
III. Evaluating Potential Side Effects
Before starting any medication, one must be aware of the potential side effects that may occur during treatment. This section will discuss the possible adverse reactions associated with Ampicillin and guide how to manage them effectively.
A. Common Side Effects
As with most antibiotics, some common side effects may arise when taking Ampicillin. These can include:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Rash or itching
- Mild stomach pain or cramps
- Dizziness or headache
Although usually temporary and self-resolving, if the symptoms of mild stomach pain or cramps, dizziness, or headache persist or worsen over time, it is essential to seek medical advice. However, if they continue or deteriorate over time, it's crucial to consult your healthcare professional for advice.
B. Serious Side Effects and Allergic Reactions
In rare instances, more severe side effects might occur while taking Ampicillin. If you experience any of the following symptoms during treatment, seek immediate medical attention:
- Chest pain or difficulty breathing
- Anaphylactic reaction (severe allergic response) is characterized by the rapid onset of swelling in various body parts, including the throat, tongue, and face, which can cause difficulty breathing and loss of consciousness.
It is critical to assess the probable consequences of Ampicillin before starting treatment, as they may differ from one individual to another. To ensure that your medication remains effective and safe, it is necessary to understand how best to store Ampicillin.
IV. Ensuring Proper Storage Conditions
Maintaining optimal storage conditions for Ampicillin is crucial to ensure its efficacy and safety. This section will guide you through the ideal storage environment, shelf life, and the expiration of this antibiotic.
A. Ideal Storage Conditions
Ampicillin should be kept in a cool environment away from direct sunlight and heat sources for optimal preservation. The recommended temperature range for storing Ampicillin is between 15°C (59°F) and 30°C (86°F). Keep the medication out of reach of children and pets to prevent accidental ingestion.
B. Shelf Life and Expiration
Like all medications, Ampicillin has an expiration date that indicates when it may no longer be effective or safe. It's essential to check the expiry date on your prescription bottle before using the medication.
- If your Ampicillin has expired, do not use it; consult with your healthcare provider about obtaining a new prescription.
- Using expired antibiotics can lead to reduced effectiveness against bacterial infections or even cause harm due to potential chemical changes in the drug over time.
- Always store Ampicillin according to manufacturer guidelines on packaging labels or inserts to maintain maximum potency throughout its shelf life.
Tips for Safely Disposing of Expired Medications:
- Contact your local pharmacy: Many pharmacies offer free take-back programs where they safely dispose of unused medications like antibiotics without harming the environment. Discover more information on these initiatives here.
- The FDA has published a guide on safely disposing of expired or unused medications at home, which can be found here. You can find the FDA's disposal recommendations here.
Ensuring proper storage conditions for your Ampicillin will help maintain its effectiveness and safety throughout its shelf life. Always check expiration dates before using any medication, and follow appropriate disposal methods when necessary. It is important to note that Ampicillin is a prescription medication and should only be taken under the guidance of a healthcare provider. Additionally, it is commonly used to treat bacterial infections and works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria by preventing the formation of their cell walls. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is the lowest concentration of a drug that can inhibit the growth of bacteria. Your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment based on your specific condition and medical history.
To optimize its effectiveness and safety, it is crucial to guarantee appropriate storage circumstances for Ampicillin. It is also essential to monitor treatment progress when using this medication.
Proper storage conditions are crucial for maintaining the efficacy and safety of Ampicillin. Ampicillin should be kept in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and heat sources at temperatures between 15°C (59°F) and 30°C (86°F). Always check expiration dates before using any medication, follow appropriate disposal methods when necessary, and consult with your healthcare provider about obtaining a new prescription if it has expired.
V. Monitoring Treatment Progress
Monitoring progress while taking Ampicillin is crucial to ensure it works effectively and safely for your medical condition. In this section, we will discuss the importance of tracking treatment progress, signs that indicate improvement or worsening of the infection, and when to consult a healthcare professional.
A. Importance of Tracking Treatment Progress
Regularly monitoring your symptoms and overall health during antibiotic therapy helps you determine if the medication is working as intended or if adjustments are needed in dosage or duration. Monitoring for any adverse reactions can assist in detecting potential problems quickly, thus allowing a healthcare professional to take prompt action.
B. Signs Indicating Improvement or Worsening of Infection
- Improvement: A decrease in fever (if present), reduced pain and inflammation at the site of infection, increased energy levels, and an overall sense of well-being typically signify that Ampicillin successfully treats your bacterial infection.
- Worsening: Persistent fever despite medication use, increasing pain or swelling at the site of infection, and new symptoms appearing after starting treatment with Ampicillin may indicate that either the bacteria causing your illness are resistant to this particular antibiotic or another underlying issue requires attention from a healthcare professional.
C. When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
If you notice any signs indicating that your condition might be worsening rather than improving while taking Ampicillin or if you experience severe side effects, it's essential to contact your doctor immediately for guidance on how best to proceed with treatment. Some situations warranting consultation include:
- No noticeable improvement within two days after beginning antibiotic therapy;
- New onset of severe side effects, such as difficulty breathing or swallowing, severe diarrhea with blood or mucus, or a rash that spreads quickly;
- Signs of an allergic reaction to Ampicillin (e.g., hives, swelling of the face/lips/tongue/throat);
- Development of new symptoms after starting treatment.
In conclusion, monitoring your treatment progress while taking Ampicillin is crucial to ensure the medication works effectively and safely for your specific medical condition. If you notice any signs of improvement, worsening of the infection, or experience severe side effects, consult a healthcare professional immediately.
Monitoring treatment progress while taking Ampicillin is essential to ensure it works effectively and safely for your specific medical condition. Signs indicating improvement or worsening of the infection should be tracked. A healthcare professional should be consulted if there are no noticeable improvements within two days after beginning antibiotic therapy or if new symptoms appear after starting treatment.
VI. Ampicillin for Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Ampicillin is an antibiotic frequently utilized to address UTIs triggered by vulnerable microorganisms. UTIs are widespread ailments that impact many individuals annually, with females being more prone to these infections than males. The primary cause of UTIs is the presence of harmful bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E.coli), which can enter and multiply within the urinary system.
A. Effectiveness of Ampicillin for UTI Treatment
Ampicillin belongs to the penicillin group of antibiotics and inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis, ultimately leading to cell death. It has been proven effective against various gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria responsible for causing UTIs. Despite its effectiveness, some strains of bacteria have become resistant to Ampicillin due to improper or overuse of antibiotics.
The effectiveness of Ampicillin in treating a specific UTI depends on several factors, including minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values - an indicator showing how much drug is needed to inhibit bacterial growth - and whether the infecting organism is sensitive or resistant to this particular antibiotic.
B. Dosage Recommendations for Ampicillin in Treating UTIs
Your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate dosage based on your age, weight, kidney function, severity/type of infection you're experiencing, and any other relevant medical conditions you may have. Generally speaking:
- Adults: The typical dose ranges from 250 - 500 mg, taken orally every six hours for seven days.
- Children: The dosage is usually calculated based on their body weight, with a standard recommendation being 25 mg/kg/day divided into equal doses every six hours.
It's crucial to follow your healthcare provider's instructions and complete the entire course of treatment even if you start feeling better before finishing the prescribed medication. This helps eliminate all bacteria and reduces the risk of developing antibiotic resistance.
C. Potential Side Effects and Precautions
As with any medication, Ampicillin may cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects include:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Rash or itching
- Mild stomach pain or cramps
If you experience severe diarrhea, persistent vomiting, difficulty breathing, face/lips/tongue/throat swelling, or signs of an allergic reaction (such as hives), seek immediate medical attention. These could be symptoms of a more serious issue.
Ampicillin should not be used by those with previous allergic reactions to penicillin or other beta-lactam antibiotics. Additionally, inform your healthcare provider about any medications you're currently taking - including over-the-counter drugs - to avoid potential drug interactions.
Ampicillin is a helpful medicine for urinary tract infections but should be used cautiously to dodge any possible adverse reactions. Next, let's look into the functioning of ampicillin to comprehend its operation more clearly.
Ampicillin is a valuable antibiotic for treating UTIs caused by gram-positive bacteria, with dosage and duration of treatment varying depending on factors such as the patient's risk profile. The appropriate dosage and duration of treatment depend on various factors, and it's crucial to complete the entire course of medication prescribed by your healthcare provider to prevent antibiotic resistance or recurrent infection. Knowing your risk factors can help prevent future UTIs.
VII. Ampicillin Mechanism of Action
Its effectiveness against various bacterial infections can be attributed to its unique mechanism of action, which involves disrupting the synthesis of bacterial cell walls. In this section, we will delve into how Ampicillin works at a molecular level and explore its minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values for different bacteria.
A. Disrupting Cell Wall Synthesis
The primary target of Ampicillin is an enzyme called transpeptidase, also known as penicillin-binding protein (PBP). PBPs are essential for forming and upkeep bacterial cell walls, as they catalyze the linking of peptidoglycan molecules. Peptidoglycans are important structural components that provide strength and rigidity to the cell wall.
Ampicillin mimics one of the natural substrates for PBPs - D-Alanyl-D-Alanine dipeptide - allowing it to bind with high affinity to these enzymes. As a result, it inhibits their activity and prevents cross-linkage formation in peptidoglycan chains. This leads to weakened cell walls that cannot withstand osmotic pressure changes within cells, ultimately causing lysis or rupture of bacterial cells.
B. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration Values
The MIC value represents the lowest concentration at which an antibiotic effectively inhibits visible growth (in vitro) after a specified incubation period. MIC values help determine the susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotics and can guide healthcare professionals in selecting appropriate treatments.
For Ampicillin, MIC values vary depending on the targeted bacteria. For example:
- Streptococcus pneumonia: 0.016 - 1 g/mL
- Escherichia coli: 2 - >256 g/mL (depending on resistance)
- Listeria monocytogenes: 0.5 - 32 g/mL (depending on resistance)
Lower MIC values generally indicate higher sensitivity to Ampicillin, while higher values suggest reduced effectiveness or potential resistance. Healthcare providers must consider these factors when prescribing antibiotics like Ampicillin to ensure optimal treatment outcomes.
C. Resistance to Ampicillin
Bacterial resistance against antibiotics such as Ampicillin is an ongoing concern worldwide due to misuse and overuse of these medications. Resistance mechanisms include the production of lactamase enzymes that break down penicillins before they can exert their effect, alterations in PBPs that reduce binding affinity for the antibiotic, and changes in membrane permeability that limit drug uptake into bacterial cells.
To combat this issue, patients and medical professionals must use antibiotics responsibly by strictly adhering to prescribed dosages and durations while avoiding unnecessary usage whenever possible.
Ampicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic, obstructs the formation of bacterial cell walls, thus restraining microbial growth and propagation. Pregnant women should be aware of any potential hazards of taking ampicillin while expecting.
Ampicillin is an antibiotic that disrupts bacterial cell wall synthesis, leading to its destruction. It targets specific enzymes involved in peptidoglycan synthesis, leading to unstable cell walls rupturing under osmotic pressure differences between internal and external environments. Always consult a healthcare professional before using any medication like Ampicillin to avoid contributing to antibiotic resistance development among pathogens.
VIII. Ampicillin Contraindications
While ampicillin is widely used, it's essential to be aware of specific contraindications that may prevent its use in some individuals. This section will discuss the most common contraindications for ampicillin and guide how to proceed if you fall into one of these categories.
A. Allergies and Hypersensitivity Reactions
You must avoid taking this medication if you have a known allergy or hypersensitivity to penicillin or any other ampicillin component. Allergic responses can vary from minor skin irritation to potentially lethal anaphylaxis. Before beginning treatment with ampicillin, speak to your healthcare provider if you are unsure whether you have a penicillin allergy. They may recommend alternative antibiotics like ciprofloxacin or azithromycin.
B. Infectious Mononucleosis (Mono)
Ampicillin should be avoided in individuals who have been identified with infectious mononucleosis (mono) resulting from the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), as taking ampicillin during mono-infection increases the likelihood of developing a non-allergic rash known as "ampicillin rash." This is because using ampicillin during mono-infection increases the risk of developing a non-allergic rash called "ampicillin rash." Instead, your healthcare provider might prescribe another antibiotic, such as nitrofurantoin, or recommend supportive care and symptom management.
C. Severe Liver Disease
Your healthcare provider may advise against ampicillin if you have severe liver disease. The liver plays a crucial role in metabolizing and eliminating drugs from the body so impaired liver function can lead to increased drug levels and an increased risk of side effects. In such cases, alternative antibiotics with less potential for hepatic toxicity should be considered.
D. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Considerations
Ampicillin is generally considered safe during pregnancy as it falls under pregnancy category B, meaning there's no evidence of harm to the fetus based on animal studies. Before taking ampicillin during pregnancy or breastfeeding, consult your healthcare provider to assess potential risks and benefits. They will weigh the benefits against potential threats and determine if ampicillin suits your situation.
In conclusion, while ampicillin is a widely used antibiotic that effectively treats various bacterial infections, specific contraindications must be considered before starting treatment. Always consult with your healthcare provider about these factors to ensure the safe use of this medication. It's important to note that ampicillin is effective against bacteria with a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 2 mcg/mL or less.
E. Allergy to Penicillins or Cephalosporins
Ampicillin should be avoided if you have a history of allergic reactions to penicillins, such as amoxicillin or penicillin G. Additionally, those allergic to cephalosporin antibiotics like cephalexin and cefuroxime should also exercise caution when considering Ampicillin treatment due to potential cross-reactivity between these two classes of antibiotics. If you experience symptoms like hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling in your face after taking any medication from these groups, consult your healthcare provider immediately. Check out Mayo Clinic Health System's guide for more information on antibiotic-induced allergies.
F. Kidney Impairment
Ampicillin is primarily eliminated through the kidneys; therefore, individuals with kidney impairment may require dosage adjustments under medical supervision. This helps prevent drug accumulation in the body that could lead to toxicity issues. Your healthcare provider can determine if an adjusted dose is necessary based on your situation by evaluating factors such as creatinine clearance levels and minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values against bacteria-causing infection.
G. Interactions with Other Medications
Ampicillin may interact with certain medications, leading to reduced effectiveness or increased risk of side effects. Some common drug interactions include:
- Oral contraceptives: Taking Ampicillin alongside birth control pills could reduce their efficacy and increase the risk of unintended pregnancy.
- Blood thinners (e.g., warfarin): Combining these drugs might enhance anticoagulant effects and increase bleeding risks.
- Probenecid: This medication can decrease renal excretion of Ampicillin, potentially increasing its concentration in blood plasma levels.
To avoid harmful interactions, always inform your healthcare provider about all prescription medications, over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, or supplements you are taking before starting an antibiotic regimen like Ampicillin.
In conclusion, Ampicillin is a potent antibiotic that can effectively treat bacterial infections. However, it is essential to consider the contraindications and potential risks associated with its use. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any new medication, and follow their instructions carefully to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Ampicillin contraindications include allergies to penicillin, kidney disease, and mononucleosis. Knowing the divergence between ampicillin and amoxicillin is essential to decide which remedy could be most suitable for your requirements.
Before taking ampicillin, consider potential contraindications such as allergies or hypersensitivity reactions to penicillins, EBV-caused infectious mononucleosis, severe liver disease, and pregnancy/breastfeeding considerations. These include allergies or hypersensitivity reactions to penicillins, contagious mononucleosis caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), severe liver disease, and pregnancy/breastfeeding considerations. Always consult a medical professional before beginning ampicillin therapy.
IX. Ampicillin vs. Amoxicillin: Understanding the Differences
Although Ampicillin and Amoxicillin are both penicillins, they have some key differences that impact their usage in treating bacterial infections. In this part, we will look into the distinctions between these two antibiotics to assist you in making an educated decision when selecting one of them.
A. Differences in Chemical Structure
The primary difference between Ampicillin and Amoxicillin lies in their chemical structure. While both belong to the same class of beta-lactam antibiotics, Amoxicillin has an additional hydroxyl group attached to its structure. This small change makes a significant difference in how each drug is absorbed by the body and interacts with bacteria.
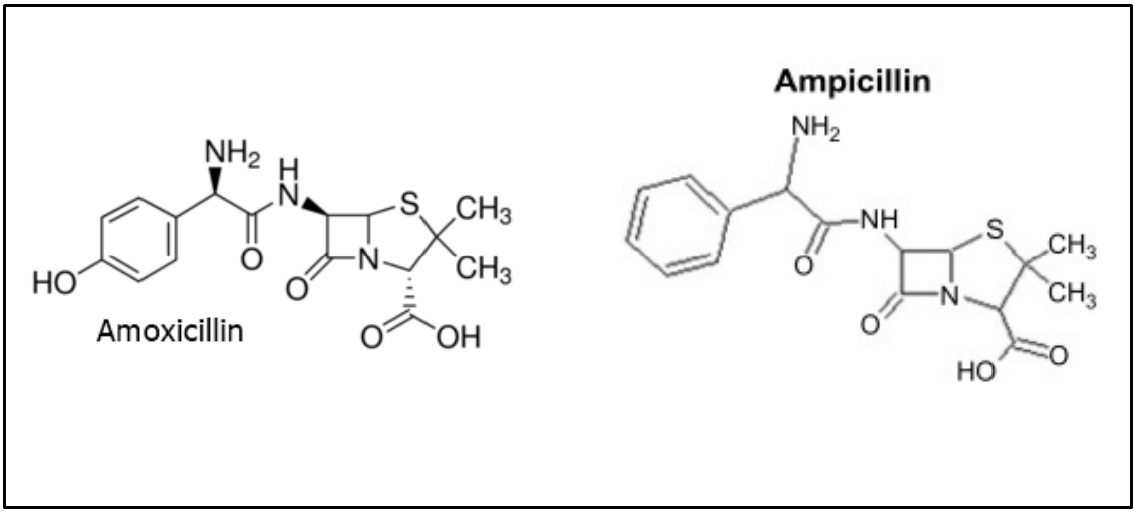
B. The spectrum of Activity against Bacteria
Ampicillin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic with activity against Gram-positive bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumonia and Staphylococcus aureus, as well as certain Gram-negative bacteria like Escherichia coli (E.coli) or Haemophilus influenza. At the same time, Amoxicillin has an even more comprehensive range of efficacy due to its superior ability to penetrate cell walls. Ampicillin has a wide range of activity against bacterial pathogens. However, Amoxicillin is even more effective due to its enhanced ability to permeate cell walls.
List of Bacteria Affected by Both Antibiotics:
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Staphylococcus aureus (non-MRSA)
- E.coli
- Haemophilus influenza
- Listeria monocytogenes (more susceptible to Ampicillin)
C. Side Effects and Interactions
Ampicillin and Amoxicillin share similar side effect profiles, the most common being gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or abdominal pain. However, Amoxicillin is generally better tolerated, with fewer reported cases of these side effects compared to Ampicillin.
Regarding drug interactions, both antibiotics can interact with other medications like oral contraceptives (reducing their effectiveness) or anticoagulants (increasing the risk of bleeding). Patients must inform their healthcare provider about all current medicines before starting treatment with either antibiotic.
D. Dosage Frequency
The differences in absorption rates and resistance to stomach acid between these two antibiotics also affect their recommended dosage frequency. Typically, Amoxicillin can be taken less frequently (usually every 8-12 hours) than Ampicillin (every 6 hours), making it a more convenient option for patients who prefer fewer daily doses (source).
In Summary:
- Ampicillin and Amoxicillin are penicillins with similar antibacterial properties but chemical structure differences.
- Amoxicillin has better oral bioavailability due to its hydroxyl group attachment, resulting in faster symptom relief.
- Amoxicillin boasts a wide range of efficacy against gram-negative bacteria compared to Ampicillin.
- Amoxicillin is more resistant to stomach acid degradation leading to higher efficacy when taken orally.
- Amoxicillin typically requires fewer daily doses than Ampicillin, making it a more convenient option for patients.
It is essential to consult with your healthcare professional before deciding which antibiotic is best suited for your specific needs. Before prescribing the most appropriate treatment plan, they will consider factors such as the type of infection, severity, and any potential allergies or contraindications.
Ampicillin and Amoxicillin, both penicillins used to treat bacterial infections, have different chemical compositions, effectiveness ranges, potential side effects, and uses. Ampicillin is effective against some bacteria, but Amoxicillin has a more excellent range of activity as it can penetrate cell walls more effectively. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all current medications before starting treatment with either antibiotic, as they can interact with other medicines like oral contraceptives or anticoagulants.
X. Buy Ampicillin Now
Overall, assessing the need for Ampicillin and understanding its dosage requirements is essential. Evaluating potential side effects, ensuring proper storage conditions, and monitoring treatment progress are crucial. Before taking Ampicillin, it is necessary to consult with a medical expert if you are planning on using the drug for UTI or while pregnant.
If you need Ampicillin, consider purchasing from Buy-Pharma.md. They offer a wide selection of affordable medications and fast shipping options. Don't hesitate to buy Ampicillin today!








































